Characteristic
Short description
The data stored in the maps can be processed by different services and for different purposes. Therefore this data is not provided by one of the other functional services, but concentrated in an own independent service.
Use
It is often useful to retrieve raw information from the map: for instance to better understand the local behavior of the services, or to allow the implementation of advanced utilities. The determination of a time zone or map segment information for an arbitrary coordinate can be named as an examples.
Retrieving time zone information
According the Coordinated Universal Time definition, the world is partitioned into diverse areas of more or less regular stripes, for which the same local time is used:
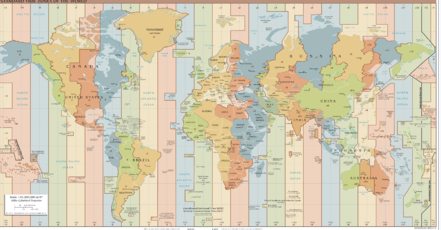
For an arbitrary coordinate on Earth the corresponding time zone can be determined. This time zone is represented by its offset to UTC or Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). Quite often the borders of such a time zone correspond to the borders of a country or state. So the finding of the correct time zone is not trivial. Besides the time zone itself, the effective time offset is of interest, i.e. the plus or minus minutes compared to Greenwich Time. According to regional regulations, daylight saving aspects playing a role, which are defined for diverse time spans. As a result, the UTC time offset depends on location in space and time.
Related Topics
| Technical Concept | FeatureLayer theme PTV_TimeZones |
| Showcase | Request the Time Zone Information |
| Integration Sample | Retrieving the Time Zone |
Retrieving road segments data
The SegmentsRequest is an abstract operation allowing to retrieve segments according to geographical criteria.
Retrieving segments information is useful to identify segments to be edited at the creation of custom Feature Layers.
It is also a necessary step to identify the combined transport![]() The combined transport is a form of transport where the vehicle in question does not drive itself but is transported by a boat or by rail (piggyback). connexions (as ferries, piggiback) that will be used as combined transport waypoints
The combined transport is a form of transport where the vehicle in question does not drive itself but is transported by a boat or by rail (piggyback). connexions (as ferries, piggiback) that will be used as combined transport waypoints![]() A waypoint is a geographic location used to specify start, destination and possible stopovers for a route..
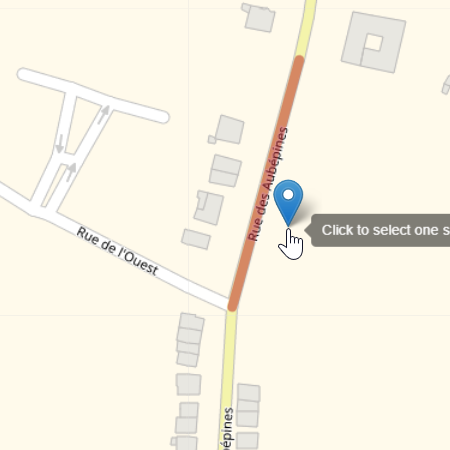
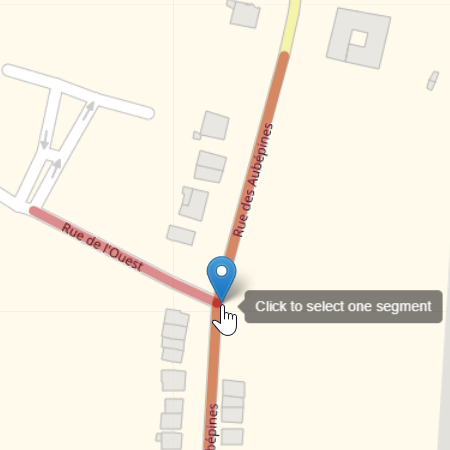
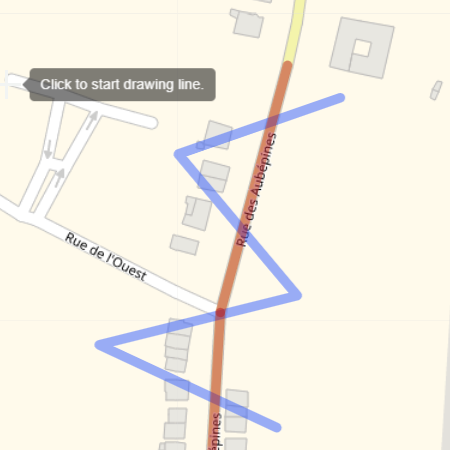
Three kinds of selectors are used to specify the geographical search.
A waypoint is a geographic location used to specify start, destination and possible stopovers for a route..
Three kinds of selectors are used to specify the geographical search.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The SegmentResponse returns a list of MapSegment
containing segmentIds, a type and other information according to the configuration of the request like the encoded geometry.
It is possible to define filter criteria in SegmentsOptions by type and by network class![]() A network class is an indicator of importance within the road segment sectioning. The road segments are divided into eight network classes by importance of the roads they represent. The network class 0 represents the most important roads, for example highways, while road segments of network class 7 are the least important roads, for example pedestrian paths. The term network level is often used synonymously, in fact the network level equals the network class plus one..
In this case, it's allow to specify for which network classes the segments shall be included in the result. If not specified, the segments will be included whatever their network class.
A network class is an indicator of importance within the road segment sectioning. The road segments are divided into eight network classes by importance of the roads they represent. The network class 0 represents the most important roads, for example highways, while road segments of network class 7 are the least important roads, for example pedestrian paths. The term network level is often used synonymously, in fact the network level equals the network class plus one..
In this case, it's allow to specify for which network classes the segments shall be included in the result. If not specified, the segments will be included whatever their network class.
Good to know
Limitations
- If a wrong geometry is used in a request a generic exception is sent.
- If a polyline intersects or a polygon surrounds more than 5 000 segments no segments are return and a specific exception is sent.
- Polygons with holes are not supported. A specific exception message will be sent.
- If no segment is found, a result limitation is sent in the response.
Data Compatibility
Custom Feature Layers are map-dependent. Indeed, the segmentIds are not the same according to the map versions. When changing maps, users will have to update their custom Feature Layers. To do this, it is advisable to store the selectors used in the segmentIds retrieval step in order to have the possibility to regenerate custom Feature Layers.
Related Topics
| Technical Concept | Custom Feature Layers |