This Technical Concept is relevant to the following Services: xRoute. Please note that both calculateReachableLocations and calculateReachableAreas require a special license.
Characteristic
Short description
The xRoute function calculateReachableLocations calculates whether one or more locations can be reached from a waypoint![]() A waypoint is a geographic location used to specify start, destination and possible stopovers for a route. or from a route
A waypoint is a geographic location used to specify start, destination and possible stopovers for a route. or from a route![]() A route corresponds to a path of a vehicle through the underlying transport network. The main attributes of a route are the distance and the time that the vehicle travels along the path. (or the other way around: route reachable from locations).
A route corresponds to a path of a vehicle through the underlying transport network. The main attributes of a route are the distance and the time that the vehicle travels along the path. (or the other way around: route reachable from locations).
The xRoute function calculateReachableAreas calculates the areas which can be reached from a waypoint or from a route, within given horizons (or the other way around, from destination to start).
For both calculations, the PTV xRoute module does not take into account the airline distance but the distance by road network.
Use
The dealer search is a common use case which needs the function calculateReachableLocations in order to detect the position of dealers within a given radius. The corridor search is an other use case, which consists in finding points (like gas stations) along a route.
The calculateReachableAreas function is designed for isolines calculation. isolines describe zones based on driving distance or travel time. The polygon returned by the calculateReachableAreas feature describes specifically this kind of zone.
The polygon returned by the reachableAreasResponse can be used for a geofencing use case.
The geofencing define virtual geographical barriers around a geographical position. For example, an integrator can trigger alerts if a vehicle![]() The term vehicle describes what is being routed or planned for. Vehicles are used in route calculation, distance matrix calculation and effectively also in tour planning. In route calculation, vehicle properties like overall size, weight and speed are in focus. In tour planning, it is vehicle properties like capacity and availability.
Commonly a vehicle is motorized, like a truck - including its trailer or a car. However also a bike or even a pedestrian are included in this definition. gets too far from its planned route.
The term vehicle describes what is being routed or planned for. Vehicles are used in route calculation, distance matrix calculation and effectively also in tour planning. In route calculation, vehicle properties like overall size, weight and speed are in focus. In tour planning, it is vehicle properties like capacity and availability.
Commonly a vehicle is motorized, like a truck - including its trailer or a car. However also a bike or even a pedestrian are included in this definition. gets too far from its planned route.
Detailed Consideration
CalculateReachableLocations
Input waypoint
The type of waypoint used determines the desired approach in the calculation of reachable locations. If a PathWaypoint is chosen, the engine triggers a corridor search using the encodedPath contained in the waypoint. For other types of waypoints, the engine triggers a dealer search around the geographical coordinates contained in the waypoint.
Options
You can provide couple of options. Please note that ReachableLocationsOptions are required due to the Horizon parameter that user must fullfill.
- Horizon gives the engine the distance or time to determine whether locations are reachable or not.
- SearchType allows the user to specify whether the engine should search if location is reachable from waypoint or if waypoint is reachable from location. The default behavior is the location reachable from waypoint (LOCATION_REACHABLE_FROM_WAYPOINT).
- TimeConsideration allows the user to calculate if locations are reachable or not at a specific date, including relevant time dependent features during the search.
- ContentSnapshotId optionally specifies a content snapshot to be used (latest content by default).
- GeographicRestrictions can also be set to restrict the reachable search during computation.
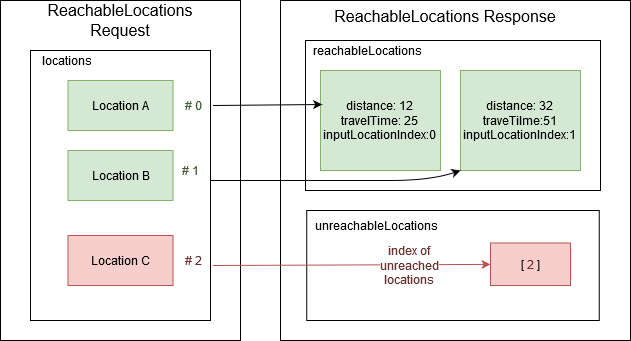
Reachable locations
From the location list sent by the user, the engine returns two tables:
- The reachableLocations table contains the list of locations that meets the conditions of reachability. Each item contains the input index of the location, its distance and traveltime from or to the given InputWaypoint.
- The unreachableLocations table contains the list of locations that do not meet the conditions of reachability. Each item in the list contains the input index of the location not reached.
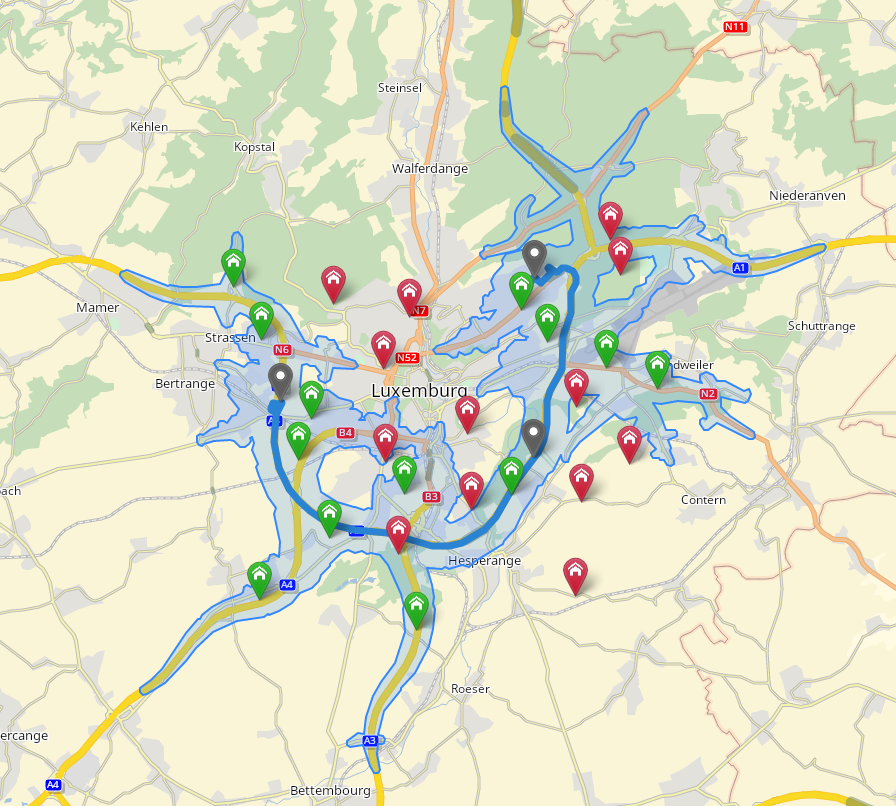
Green markers are reached locations, as opposed to red markers that are unreached locations. Every reached green marker is within the polygon returned by the calculateReachableAreas operation.
CalculateReachableAreas
Input waypoint
The type of waypoint used determines the desired approach in the calculation of reachable areas. If a PathWaypoint is chosen, the engine triggers a corridor search using the encodedPath contained in the waypoint. For other types of waypoints, the engine triggers a dealer search around the geographical coordinates contained in the waypoint.
Options
- Horizon gives the engine the distance or time to determine whether the waypoint is reachable or not.
- ReachableAreasCalculationMode specifies the calculation mode of a reachable areas calculation. There is two calculation modes: PERFORMANCE or QUALITY (default). Depending of your requirement, you may want to switch between those two modes.
- ReachableAreasDrivingDirection defines whether to calculate the areas which can be reached from the waypoint within the horizons or to calculate the areas from which the waypoint can be reached within the horizons.
- TimeConsideration allows the user to calculate if the waypoint is reachable or not at a specific date, including relevant time dependent features during the search.
- ContentSnapshotId optionally specifies a content snapshot to be used (latest by default).
- GeographicRestrictions can also be set to restrict the reachable search during computation.
Result Fields
The user can specify ReachableAreasResultFields to specify what should be returned in the response. This way, the user can request ReachableAreasSegment with ReachableAreasSegmentResultFields. Retrieved segments can contain:
- the accumulated distance and traveltime during reachable areas calculation.
- the id of each segment. It can be used in subsequent xData requests, e.g. to retrieve additional information or to create custom restrictions.
- the polyline of each segment. It can be used for client-side visualization.
- the predecessor index of each segment. With this index, the user can build the predecessors chain that separate this segment from the waypoint (waypoint can be a PathWaypoint).
Reachable areas response
The content of the response depends on the ReachableAreasResultFields of the request. The response may contain :
- The returned polygons are the reachable area for each horizon. Those polygons can contain holes.
- The returned segments are the segments reached during reachable areas computation.
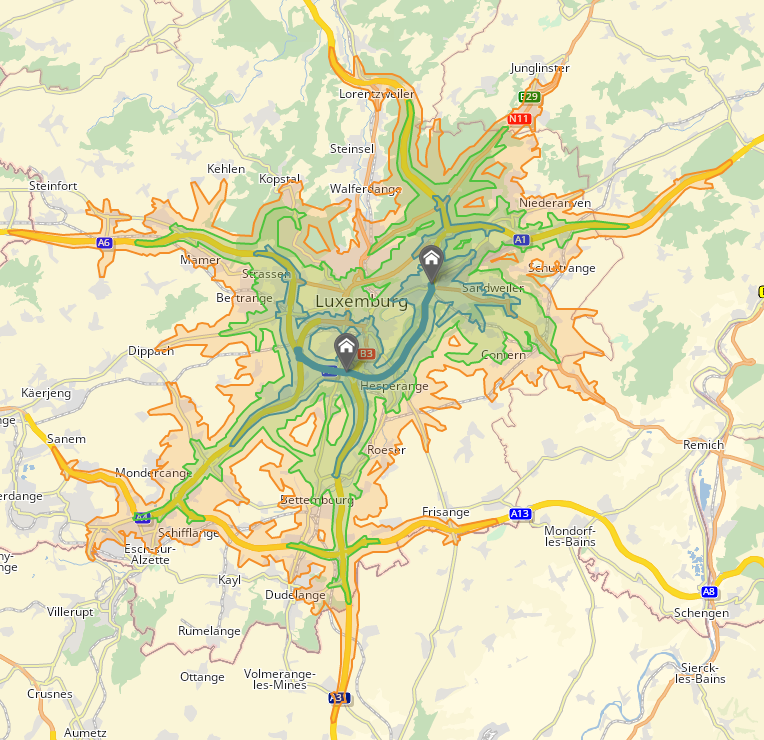
Multiples horizons can be requested and received in the same response. On the figure above, there are three colored polygons corresponding to each horizons.
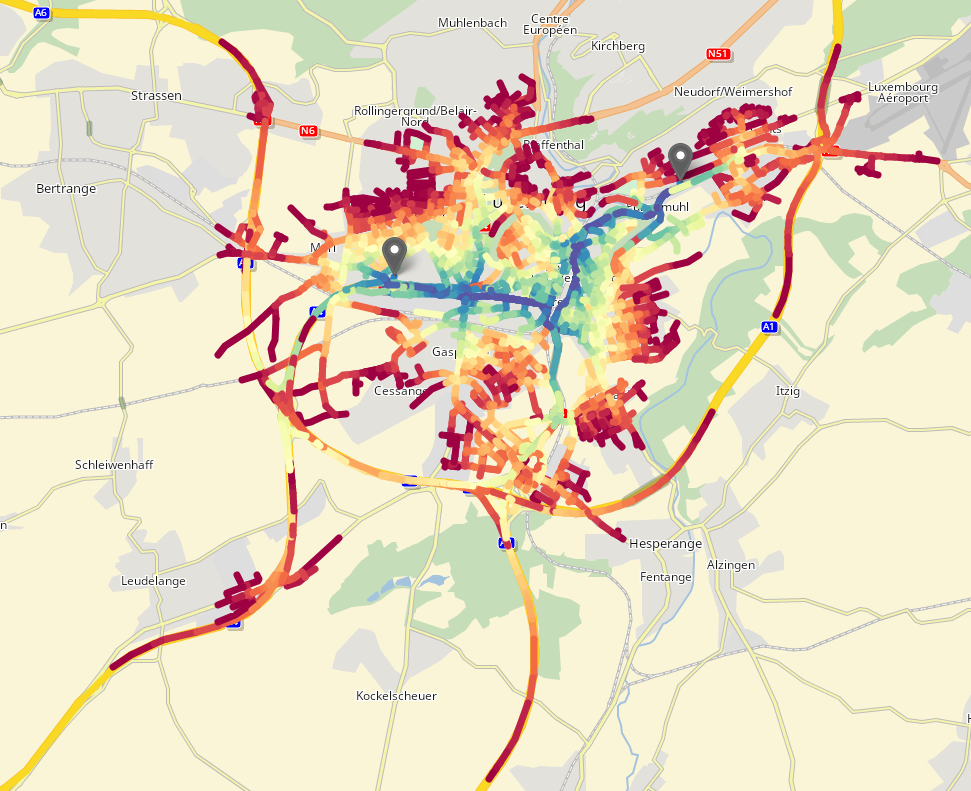
 A polyline is a continuous line composed of one or more line segments given as a set of tuples with x,y and optional z coordinates.
A polyline is a continuous line composed of one or more line segments given as a set of tuples with x,y and optional z coordinates.Polyline of reached segments can be retrieved and displayed on a heatmap to see the accumulated traveltime and distance of each segments.
Good to know
Distance returned in case of a PathWaypoint
In case of a PathWaypoint, the returned distance is the distance to the nearest node.
Predecessor index
The predecessor index of a segment is the index of the predecessor segment in the segments array. The predecessor indicates the segment that was reached before during the computation. If the segment has no predecessors (ie the predecessor was either the entry waypoint or on the path in case of a PathWaypoint), the predecessor index will be -1.
Warranty
The results obtained by isoline calculation with the calculateReachableAreas function will be the same as those obtained with the calculateReachableLocations function. For example, a RouteLocation reached by dealer or corridor search will be within the polygon returned in the ReachableLocationsResponse. However, some locations close to the polygon border may be unreached even if they belong to the polygon due to an approximation used during the polygon calculation.
Reachable segments ids can be used to create a custom feature layer. For example, a user can block all segments within 10 minutes by road of a certain position, requesting segments ids in a calculateReachableAreas request in use them to create a custom feature layer.
Limitations
ReachableAreasSegment can only be retrieved with calculationMode QUALITY.
When using a PathWaypoint as input waypoint, make sure that the encodedPath does not cross a country listed in the request GeographicRestrictions prohibited countries.
SearchSpaceBounds can't be used together with calculate reachable area or reachable locations and will result in a InvalidValueFault. The user can still clip the returned polygon with his own data and methods.
Horizon values cannot exceed a certain threshold defined in the server configuration. Distance-based horizon must have a lower value than the one defined in xroute.reachability.maximumDistanceHorizon. Travel-time-based horizon must have a lower value than the one defined in xroute.reachability.maximumTravelTimeHorizon.
Additional server restrictions (number of horizons, horizon values, path length) are applied when using a PathWaypoint. Those restrictions are defined in xroute.reachability.pathWaypointPolygon.
Additional server restrictions (number of horizons, horizon values, path length) are applied when requesting ReachableAreasSegment. Those restrictions are defined in xroute.reachability.reachableSegments.
Segments retrieval comes along with performance losses and response size increase.
The violation mechanism is not supported by reachability methods and these methods behave as if violations are disabled.
The Feature Layer PTV_RestrictionZones is not supported by reachability methods and should not be used.
Related Topics
| Showcase | Calculate Reachable Locations |
| Showcase | Calculate Reachable Areas |
| Showcase | Consider Reachable Area Inner Segments |
| Integration sample | Calculating reachable locations and areas |