Time Zones
Characteristic
Short description
According the Coordinated Universal Time definition, the world is partitioned into diverse areas of more or less regular stripes, for which the same local time is used. In consequence, these time zones define the hours and minutes the local time is ahead or behind Greenwich Mean Time in this area. According to regional regulations, daylight saving time aplies for some different time spans. As a result, the UTC time offset depends on the geographical location and the time.
Use
Time relevant parameters are used in multiple situations, especially the TimeConsideration type. It incorporates a reference time to determine which time-dependent data should be taken into consideration to calculate the response.
Fields representing time-specific parameters in the PTV xServer API are expected to contain a UTC offset, mostly due to its uniqueness. If a time zone is missing, the service tries to determine the time zone by the context of the corresponding functionality. Below the behavior is described in detail.
Detailed Consideration
According the Coordinated Universal Time definition, the world is partitioned into diverse areas of more or less regular stripes, for which the same local time is used:
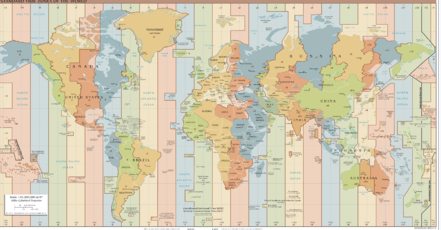
For an arbitrary coordinate on Earth the corresponding time zone can be determined. This time zone is represented by its offset to UTC or Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). Quite often the borders of such a time zone correspond to the borders of a country or state. In combination with more or less arbitrary regulations concerning daylight saving times, the determination of the UTC offset proves to be quite complex.
A point in time is always specified by a string in the format 2015-12-24T12:00:00+01:00
(which is December 24th, 2015 at 12:00 noon with an offset to UTC of +1 hour), related fields have the type XMLGregorianCalendar.
This type does not require the UTC offset to be specified, but we strongly recommend to specify it always, in order to execute operations covering
several time zones and to assign time-dependent information such as speed patterns correctly.
Handling Local Time
A point in time without a UTC offset is treated as local time. Although it is recommended to always specify a time zone, PTV xServer will automatically assign the UTC offset from the request context or throw an exception if it fails. In the following description the determination of the intended UTC offset for the planning horizon in an xTour request is used as an example. Since the planning horizon has no location, the other locations of the request are used to determine the UTC offset during the following steps:
- Determine the UTC offset for all locations: For each location of the request the time zone offset is detected (if none is given in the opening intervals of the location). If no offset can be detected because all locations lie in an ocean or in a sparsely populated area and no time zone information is available, an exception is thrown.
- If multiple offsets are detected then throw an exception: Since it is not clear which of the offsets to choose for the planning horizon, it is impossible to provide an automatic detection of an offset. So the tour planning is aborted totally.
- If all detected time zone offsets for the locations are the same, then this offset is applied to the planning horizon: No inconsistencies arise when this offset is used for the planning horizon.
This approach to determine the time zone can be applied generally, also when only one location is available, as in the case of an
opening interval in the
Site
type. The (one and only) location of the tour's site can be used to detect the missing UTC offset.
Other examples for determination of a missing UTC offset are:
- In xRoute, when a route
 A route corresponds to a path of a vehicle through the underlying transport network. The main attributes of a route are the distance and the time that the vehicle travels along the path. is calculated in combination with a time consideration and a reference time without a UTC offset:
The first or last waypoint
A route corresponds to a path of a vehicle through the underlying transport network. The main attributes of a route are the distance and the time that the vehicle travels along the path. is calculated in combination with a time consideration and a reference time without a UTC offset:
The first or last waypoint A waypoint is a geographic location used to specify start, destination and possible stopovers for a route. (according the used time consideration scenario) is used to find the missing offset.
A waypoint is a geographic location used to specify start, destination and possible stopovers for a route. (according the used time consideration scenario) is used to find the missing offset.
- In xMap, when a map is requested in combination with a time consideration and a reference time without a UTC offset: The map center and the corner points are used to find the missing offset.
- In xTour, when no planning horizon is defined: If an offset is given at any opening interval of the tour locations or at any operating/break interval of the drivers, the first offset is taken for the tour events in the response. If no offset at all is given, the tour locations are used to find an offset.
- In xDima, when a distance matrix is calculated in combination with a time consideration and a reference time without a UTC offset: The waypoints from the start locations are used to find the missing offset. If multiple offsets are detected then an exception is thrown and the distance matrix calculation is aborted totally.
- In xData, when a high-performance routing network is created in combination with a time consideration and a reference time without a UTC offset: It is not possible to determine the missing offset because several time zones can be involved in the process, an exception is thrown and the high-performance routing network creation is aborted totally.
A special case is the map rendering. The behaviour of the automatic time zone detection is slightly different and described in the following example. In this example, the rendering is performed in combination with time-dependent Feature Layer properties, but a reference time without a time zone is specified. To determine the time zone most propably intended, the center of the map and its edges are used as an array of locations and applied to the following evaluation:
- Find the set containing all locations for which a time zone can be determined: For locations in oceans or sparsely populated areas the time zone may not be determinable. These locations are excluded from the set.
- If this set is empty then a result limitation is added to the commonly calculated result: The result limitation can be regarded as a warning. Adding a wished time zone offset can be avoid the result limitation.
- If this set contains the same time zone offset for all locations, then this offset is applied to the time parameter: No inconsistencies arise when this offset is used for the time parameter.
- If this set contains differing time zone offsets, then the most frequently used offset is applied to the time parameter and a result limitation is added to the commonly calculated result: The result limitation can be regarded as a warning that the applied time zone offset may not be the intended one.
Another special case is map matching for which the UTC offsets are not determined automatically. Instead UTC offsets have to be specified with each timestamp, otherwise an exception will be thrown.
Related Topics
| Technical Concept | Time Consideration |
| Technical Concept | Orders, Locations and Stops in Tour Planning |